COTN artist guide
hello! this may be overwhelming, but its simplified best we can! feel free to just look at the visual charts for a visual example of how something may look, or read to get some further information!
TERMINOLOGY
you dont have to necessarily memorize/know these, but some terms may come up!Sire - the biologically male parent of a litter
Dam - the biologically female parent of a litter
Progenitors - the biological parents of a litter
Offspring/Progeny - the biological kittens of a pair of opposite sex cats
Gestation - the length of time a dam carries her kittens before kitting
Punnett Square - a table used to compare the sire's genes to the dam's genes in order to determine possible combinations of the genes in offspringGene - an inherited trait that may be passed to offspring
Locus - plural "Loci", the address or location of a gene pair
Allele - the symbol used to represent a single copy of a gene
Dominant - requires only one copy of the gene to be expressed, can hide other traits that may be passed to offspring
Recessive - requires two copies of the gene to be expressed and can be hidden by other traits, may be passed to offspring
Carrier - an individual that carries a trait that is not visually expressed
Co-dominant - a trait that combined with another of the same nature will be expressed separately to produce a patchwork
Incomplete Dominant - a trait that combined with another of the same nature will be expressed partially, either as a perfect mix or an inequal mix, depending on the nature of the genes involved
Sex-linked - a trait that is attached specifically to the X chromosome resulting in unique inheritance, expression is directly related to biological sex
Chromosome - a structure where the genetic information is housed, they occur in identically shaped pairs but may contain gene variations from each other, the chromosomes that determine biological sex are unique in that the Y chromosome is not identical to its X chromosome pair partner, it is much smaller and contains much less genetic information
Homozygous - has 2 copies of the same allele on a locus, an individual that is homozygous for a trait is called a homozygote in reference to that trait
Heterozygous - has 2 different alleles on a locus, an individual that is heterozygous for a trait is called a heterozygote in reference to that trait
Genotype - a code of alleles arranged in gene pairs to represent the traits an individual expresses and carries
Phenotype - the physical expression of an individual's genotype, a trait that is expressed is not always visible such as a congenital condition
Congenital Condition- a health condition inherited genetically from biological parents
Chimera - an individual that expresses two fully independent genotypes within the same body, usually as a result of two embryos fusing early in development
Somatic Mutation - an uninherited mutation in a skin cell or cluster of skin cells that happens after an embryo begins to develop, such as a mole or birth mark, that then grows black fur
THE BASICS
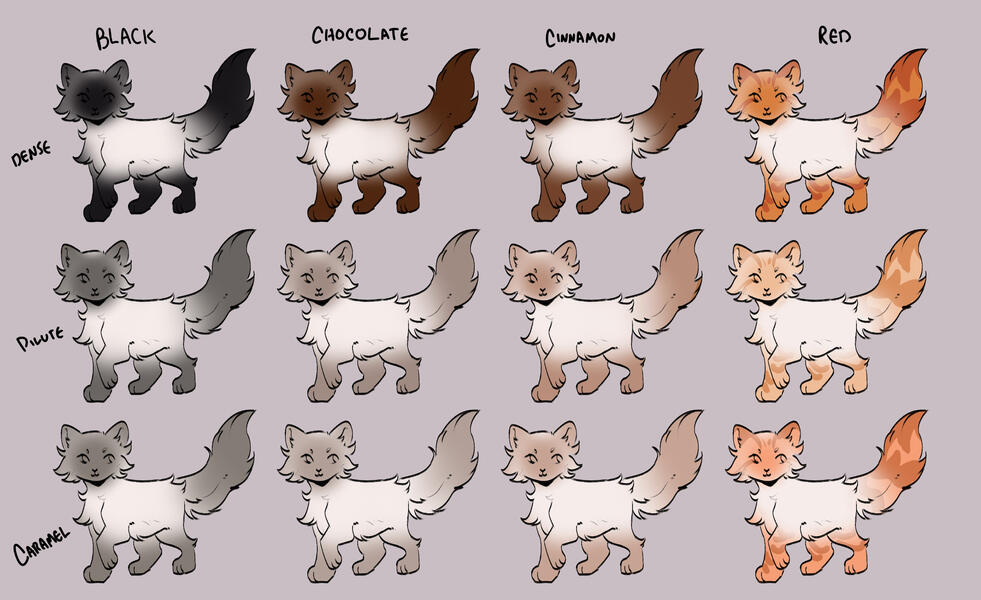
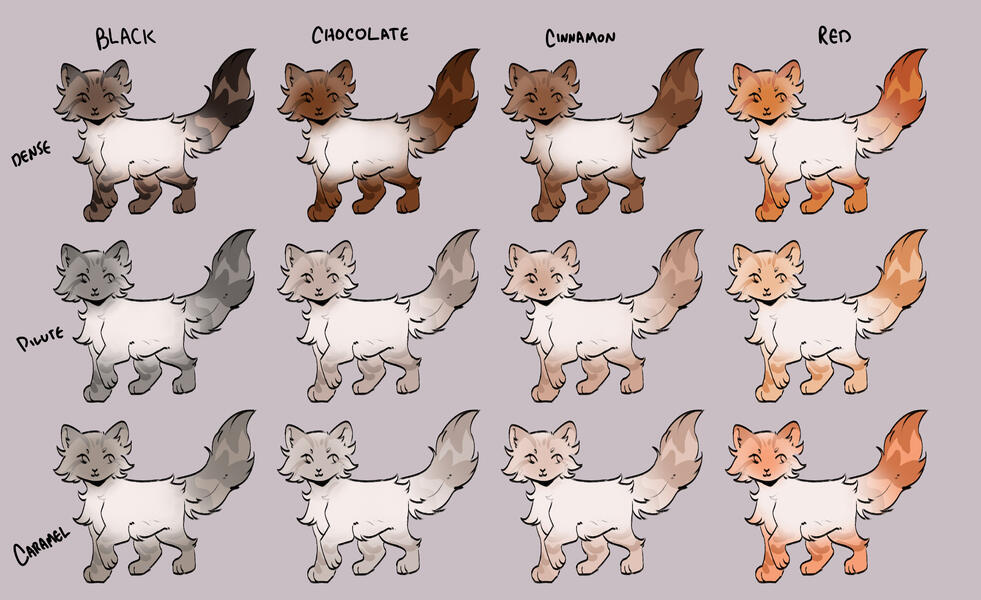
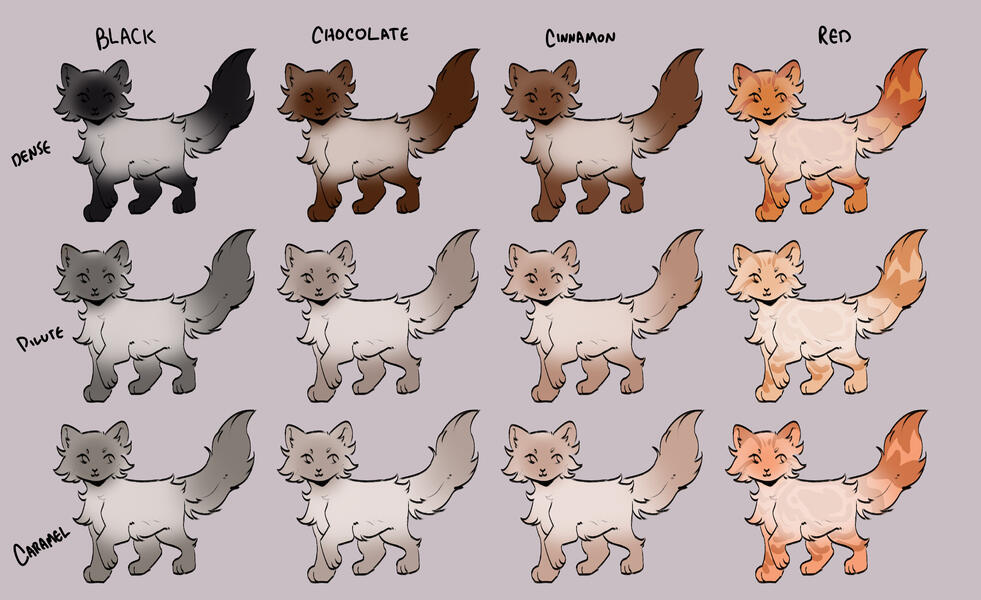
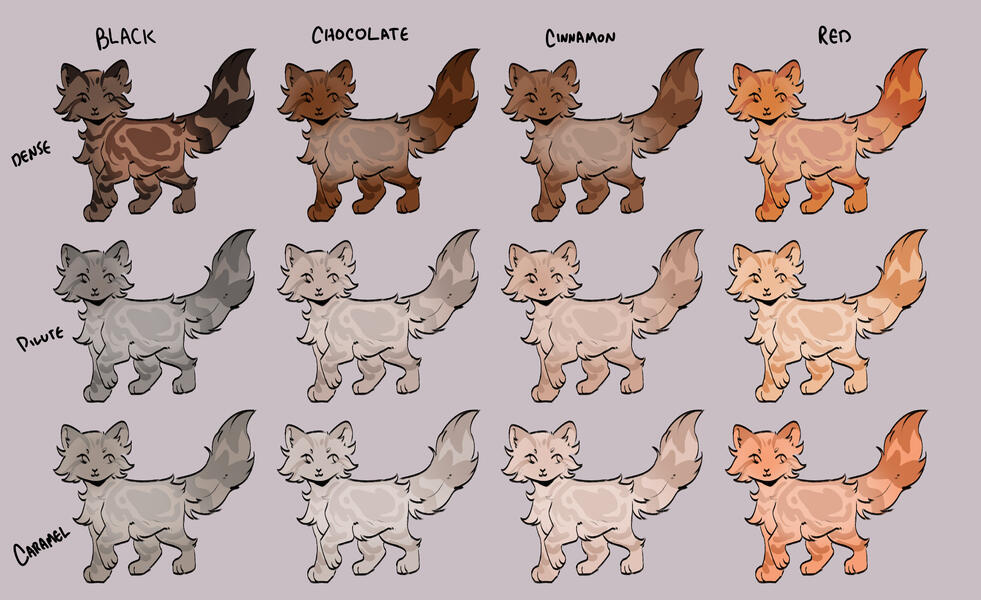
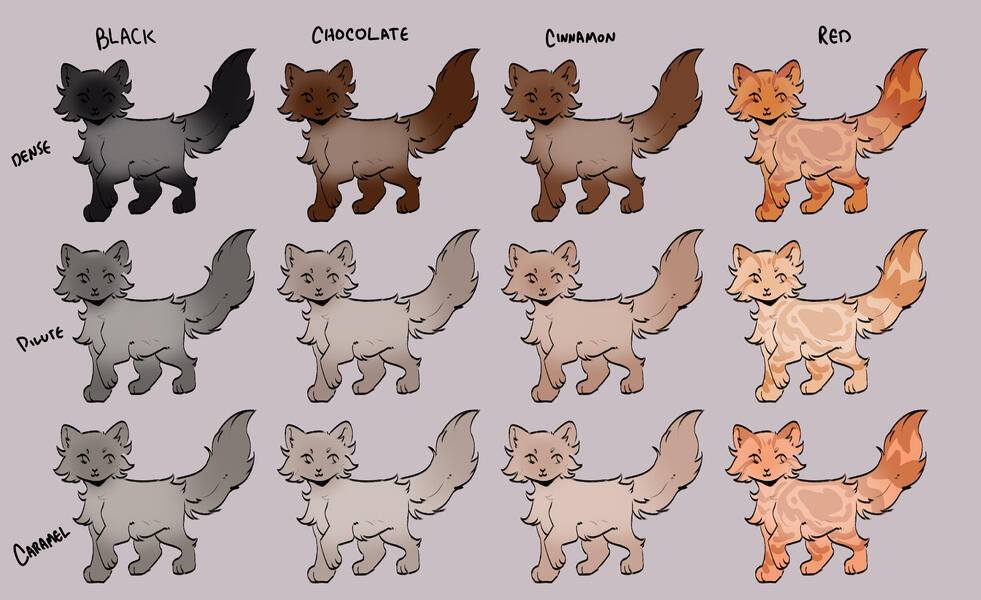
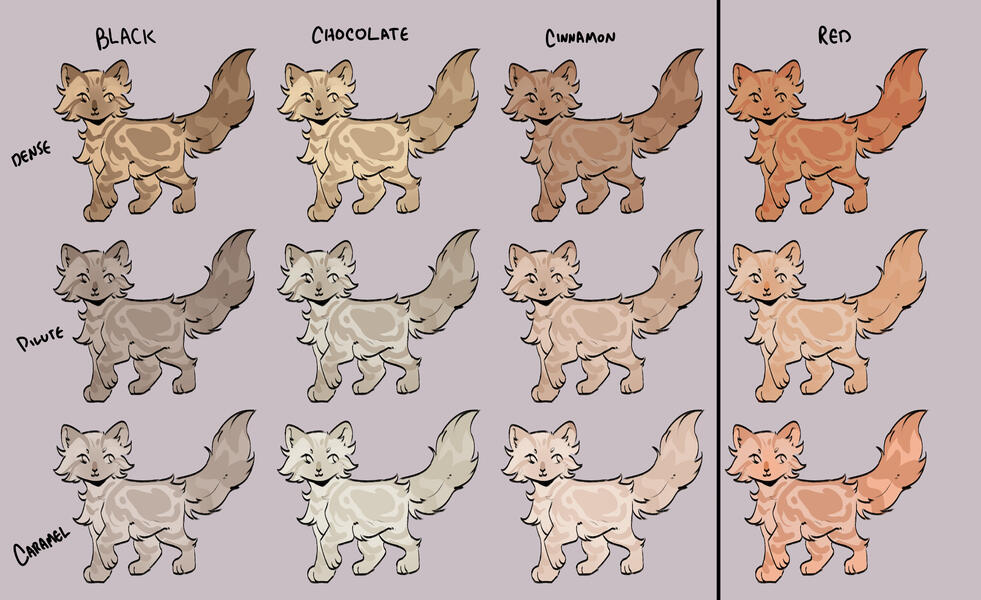
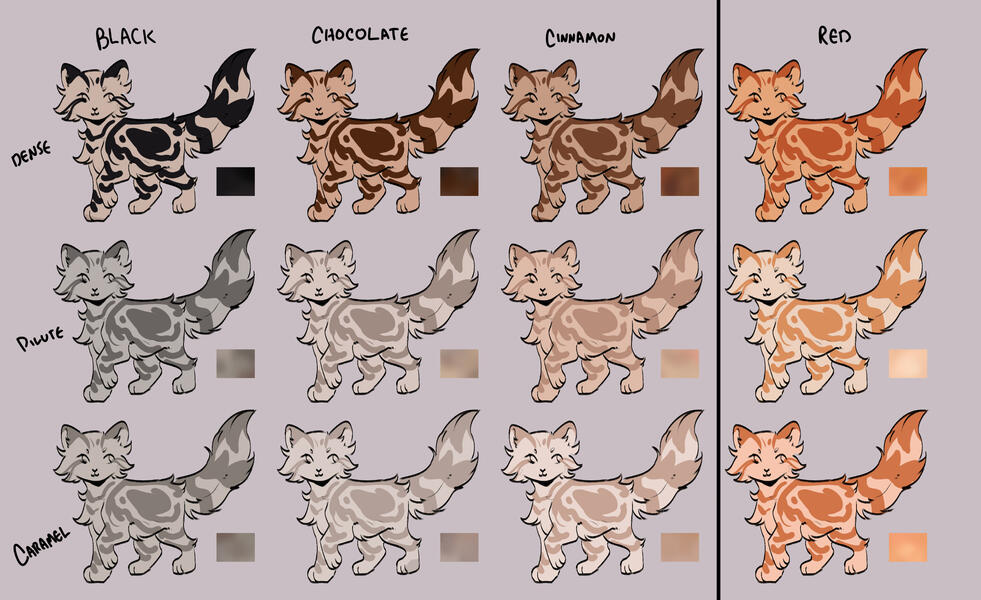
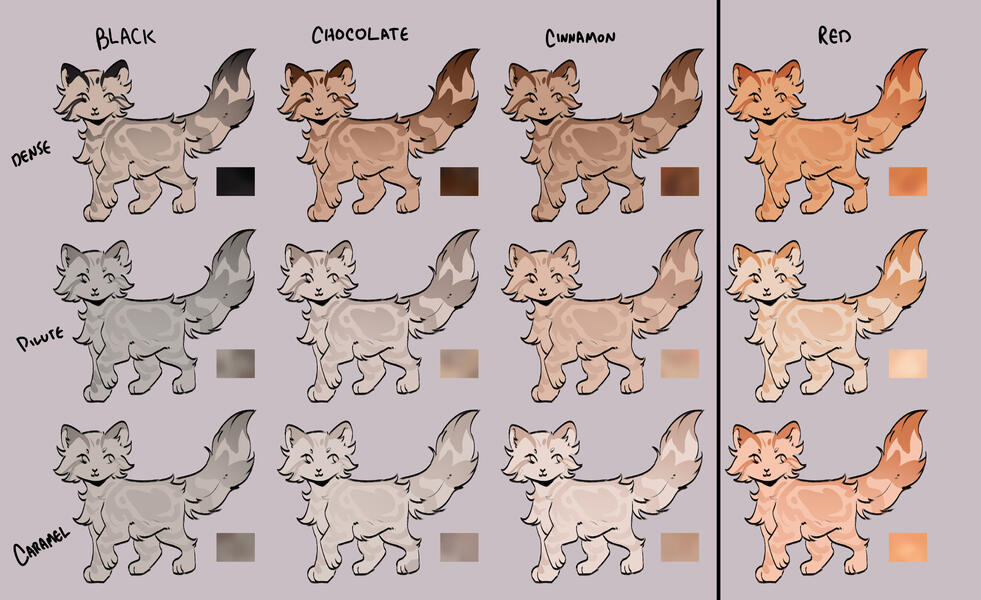
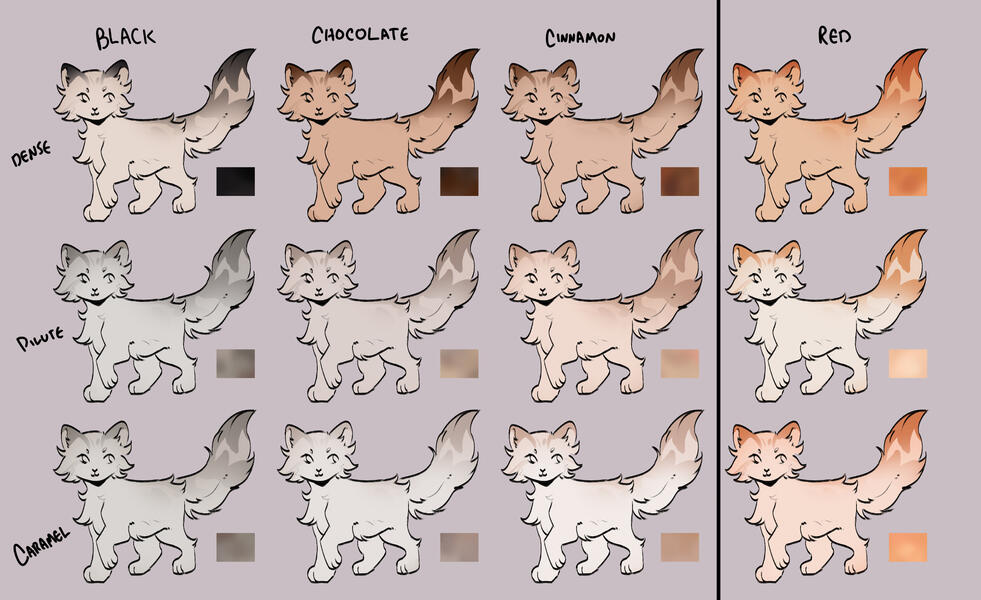
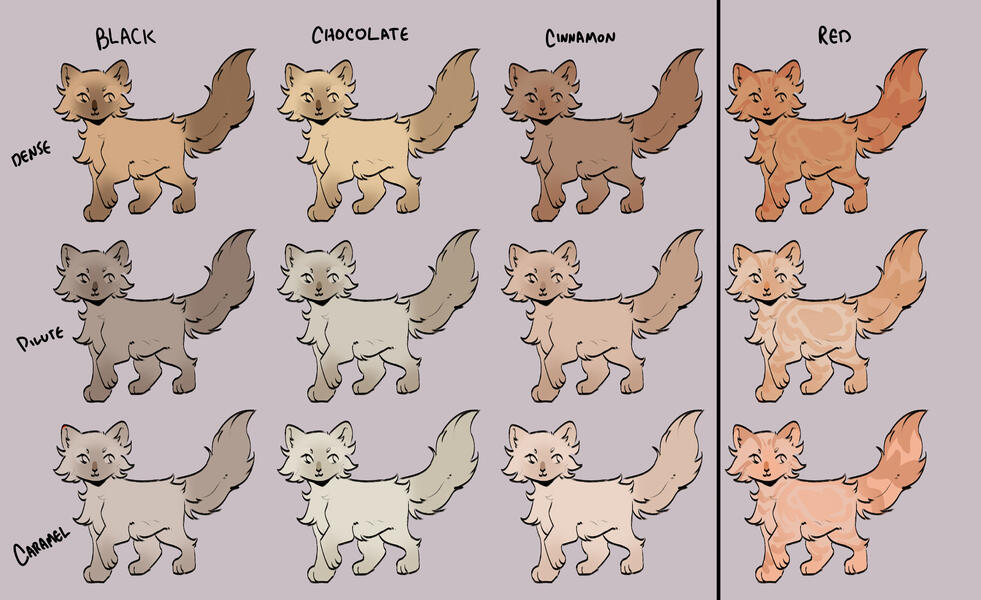
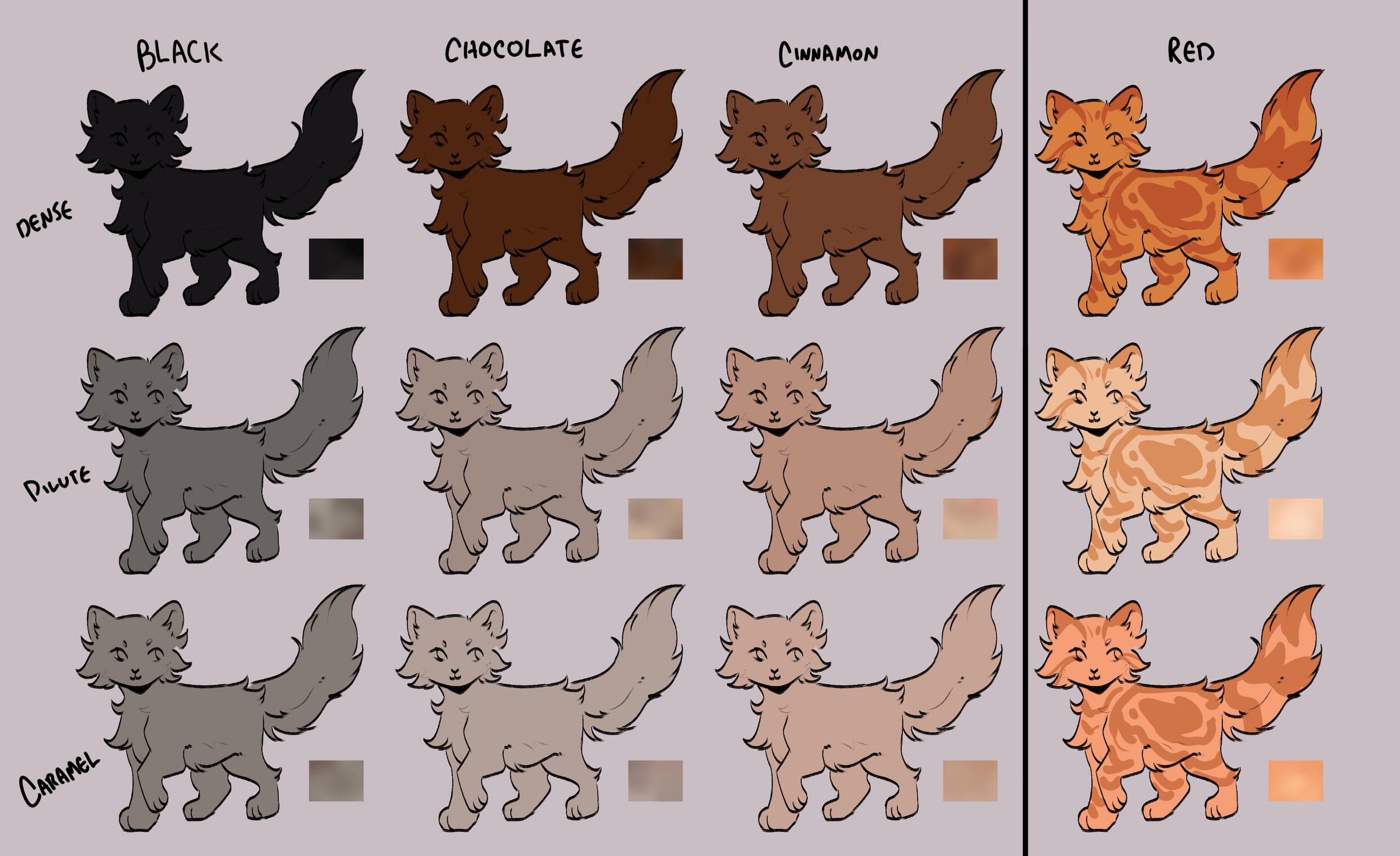
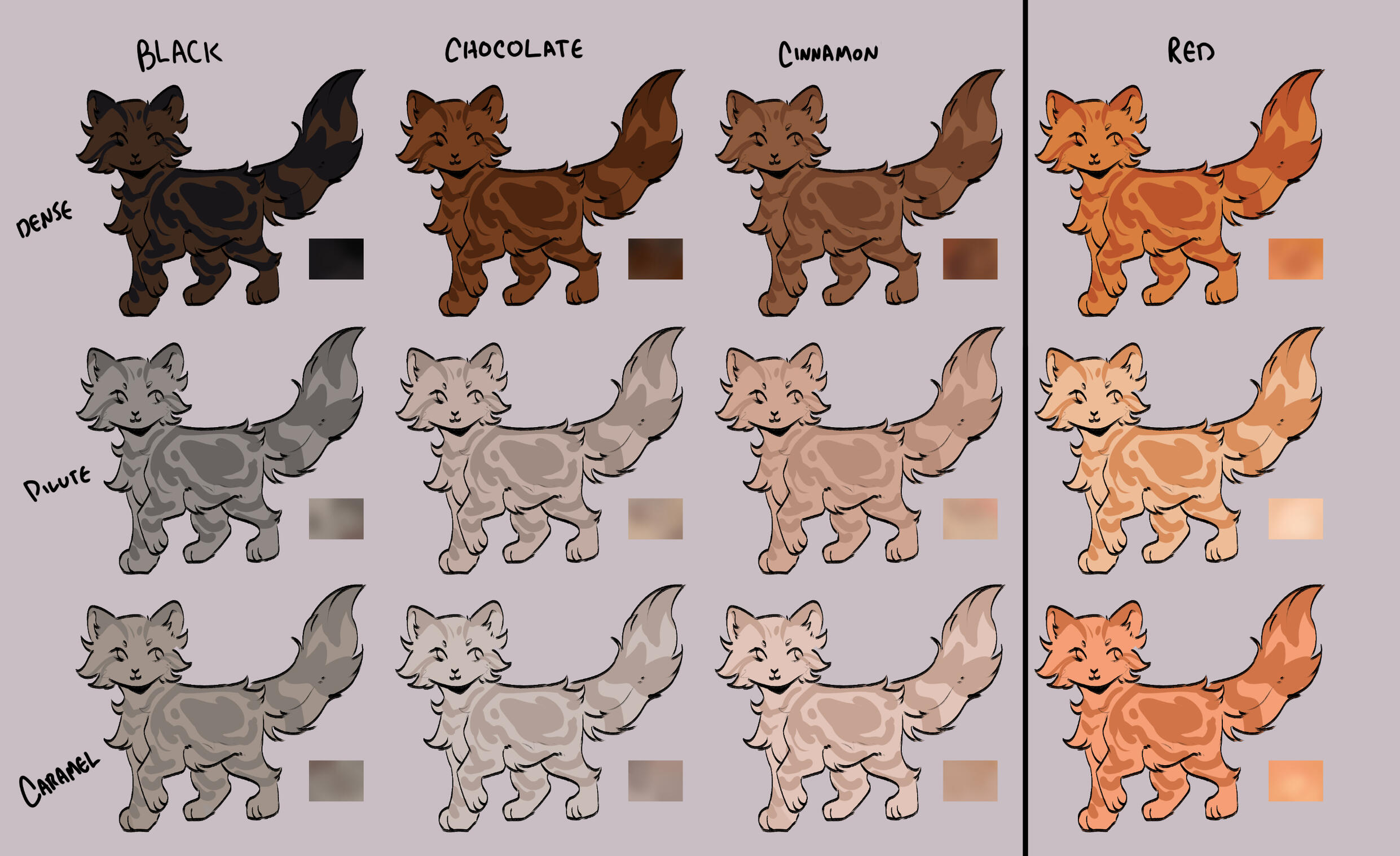
lets start with the basics: solids, and tabbies.solids/selfs are genetically non-agouti. for COTN use, call these solid or self!
tabbies are genetically agouti. for COTN use, call them tabby!all cats are either black based [B] or red based [XO].
cats can either be dense, dilute, or caramelized.black [BB] turns into blue, turning into caramel-based blue / caramel.
(google: 'black cat/brown tabby' / 'oriental shorthair blue' / 'oriental shorthair caramel')chocolate [bb] turns into lilac, turning into caramel-based lilac / tan (or fallow).
(google: 'havana brown cat' / 'oriental shorthair lilac' / '???')cinnamon [b1b1] turns into fawn, turning into caramel-based fawn / taupe.
(google: 'cinnamon british shorthair' / 'oriental shorthair fawn' / '???')and red [XO] turns into cream, turning into caramel-based cream / apricot.
(google: 'orange cat' / 'cream tabby cat' / '???')
- note reds are ALWAYS tabbied. they can be genetically solid, but they will always show tabby marks
tabby marks are always the colour of what they are genetically, which is why most of your classic 'brown tabbies' are actually black - because their stripes are black!blacks take on a brownish hue, and rarely ever black (except with some other modifiers, which we will get to later!)
** note these are all rough guide colours. colours of cats can vary quite a bit, you can colour pick from here or other COTN cats or try your own interpretation of the colour!


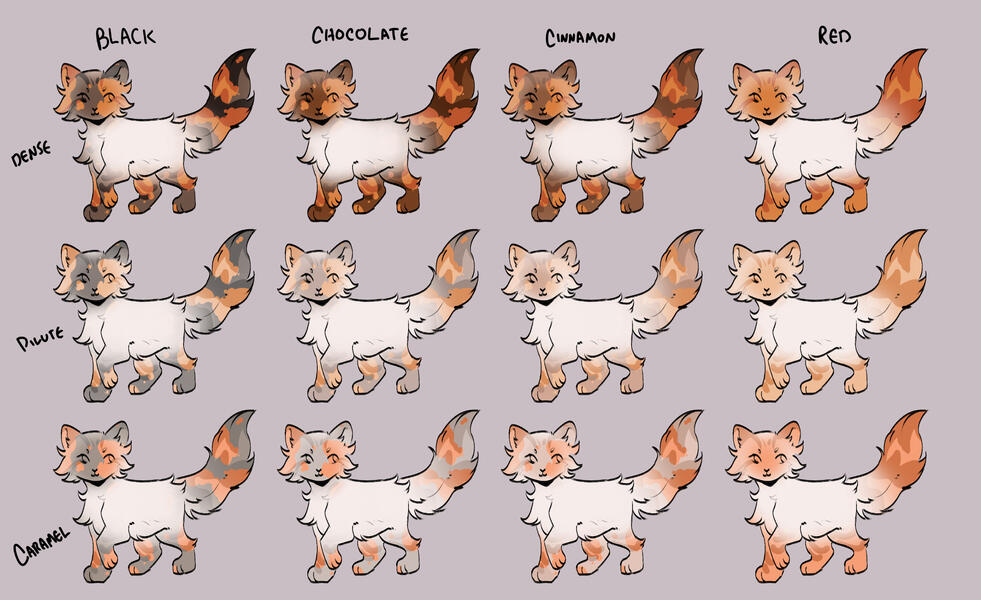
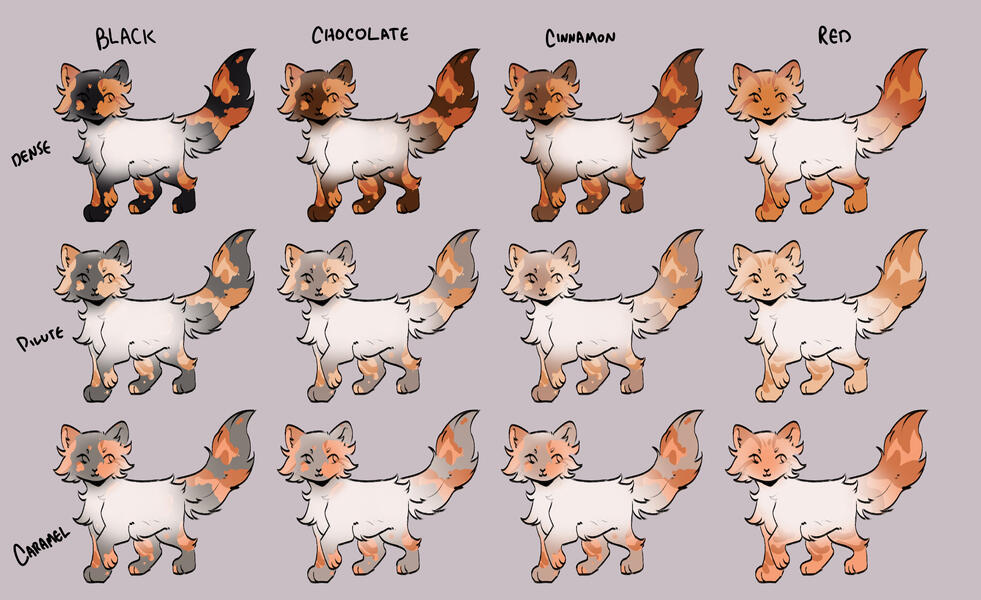
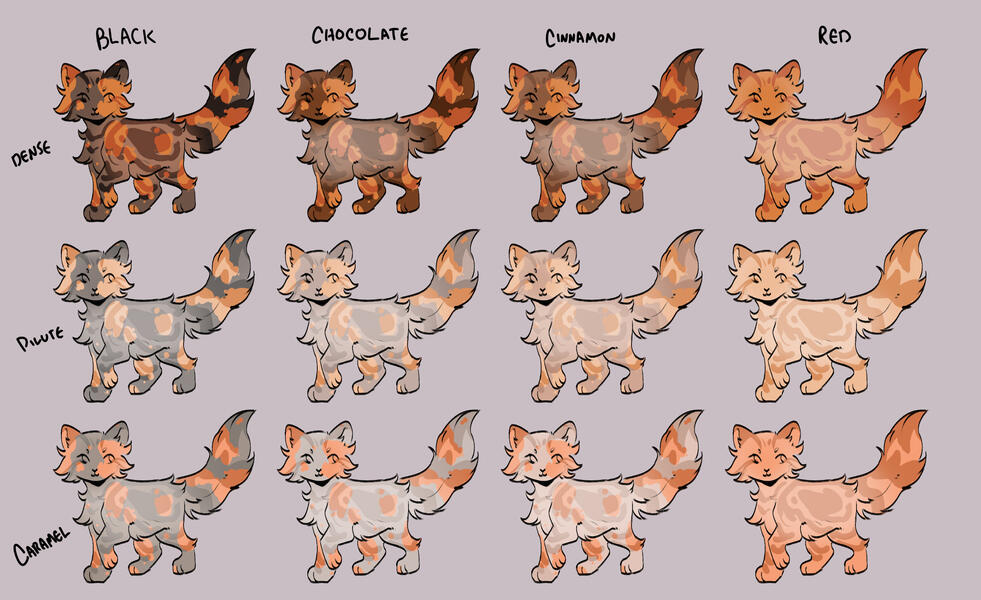
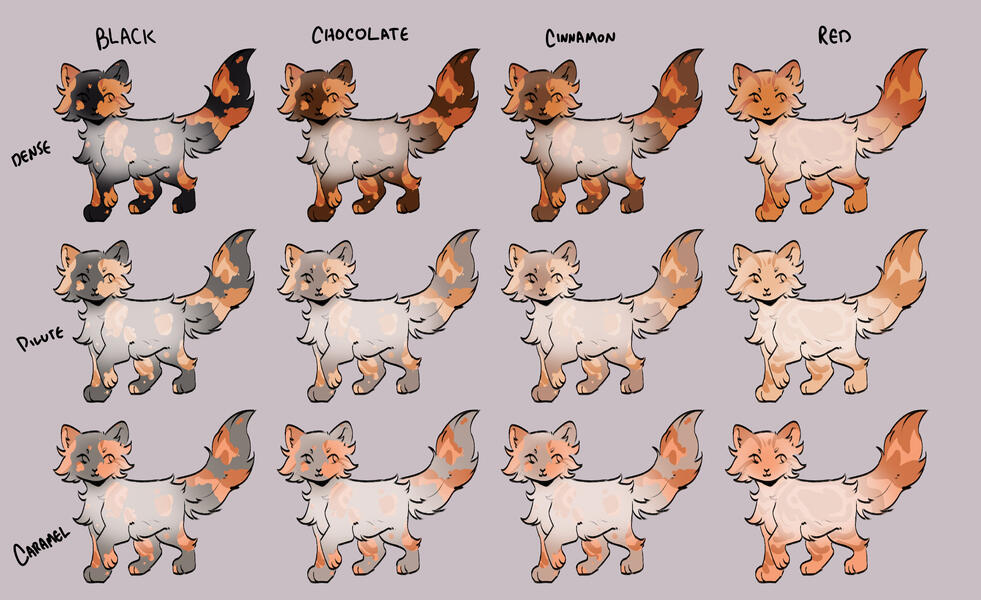
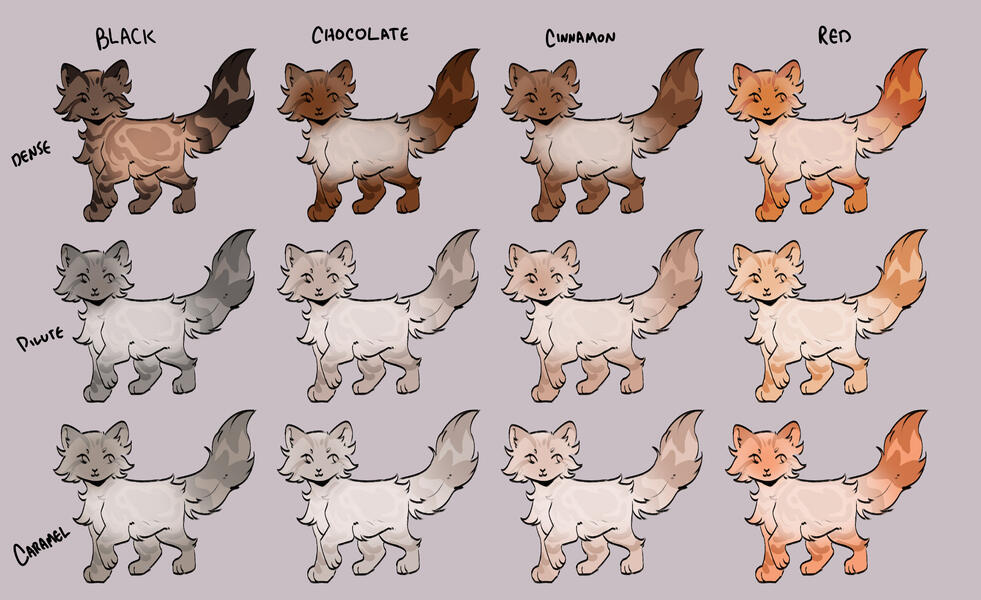
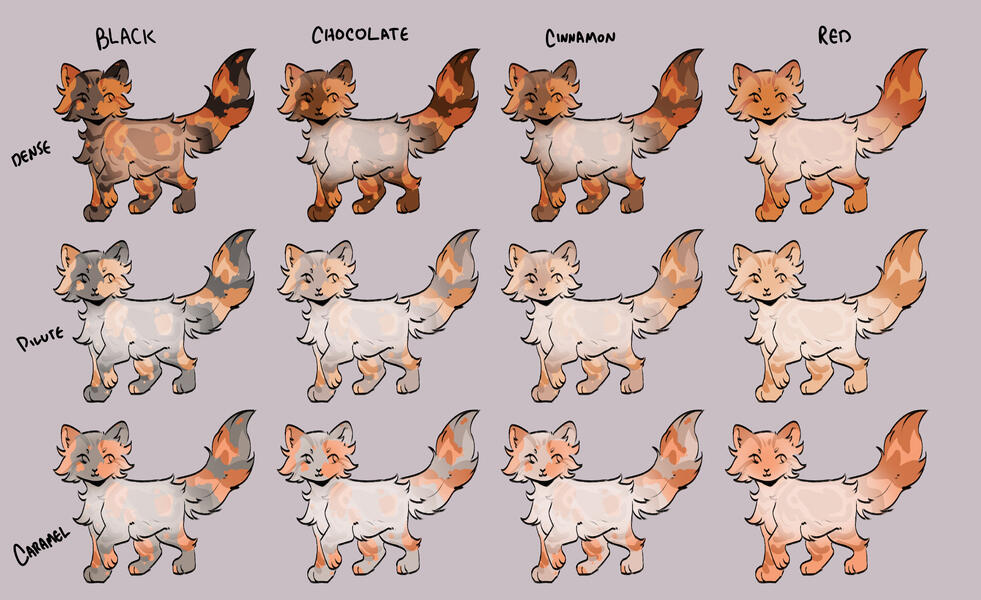
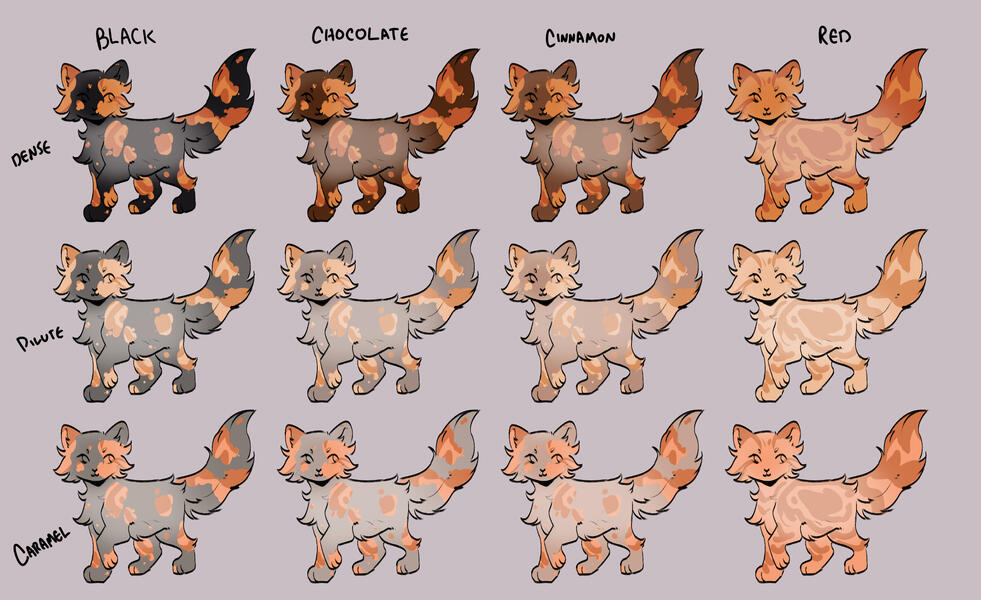
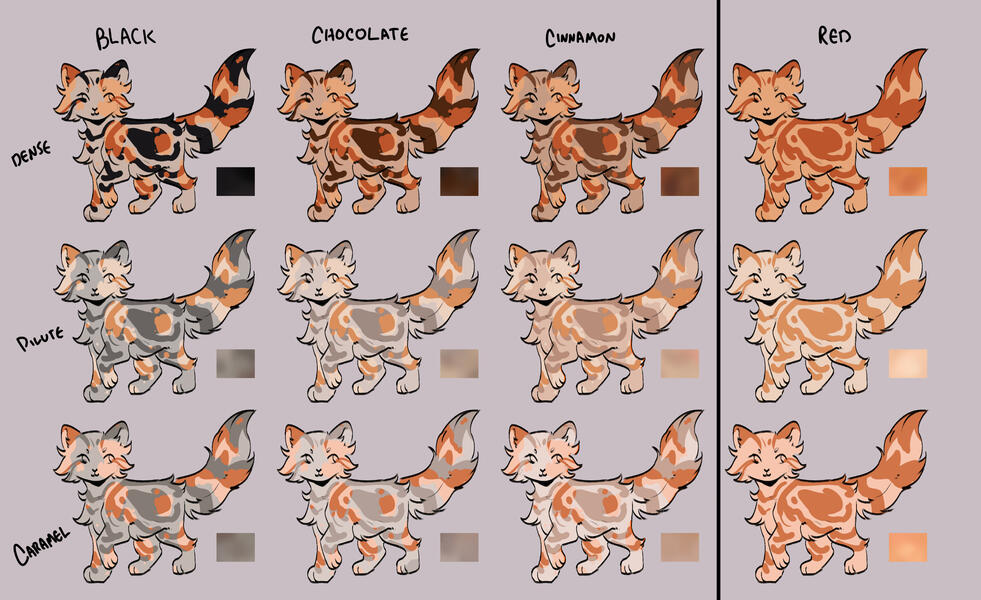
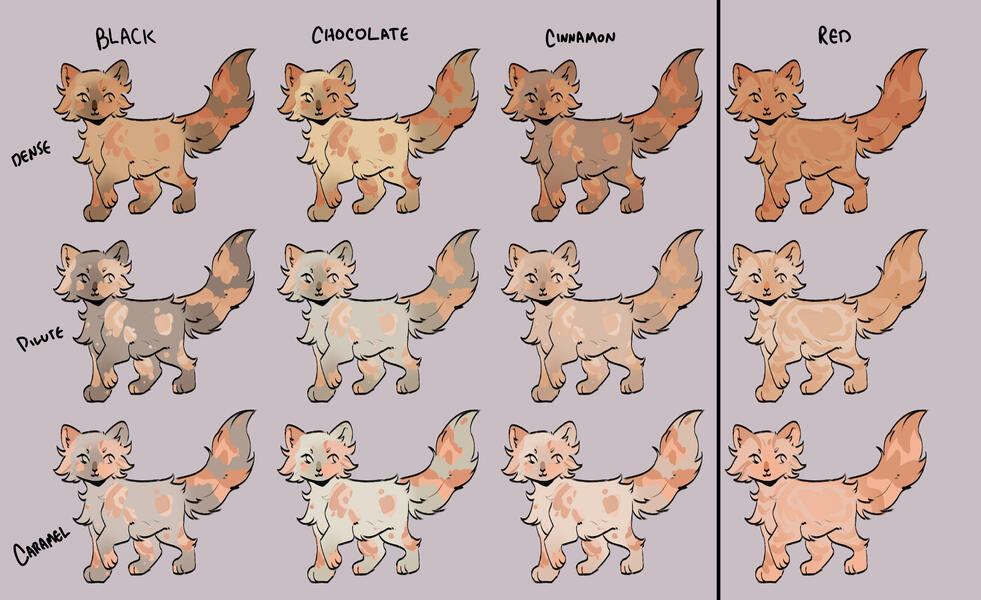
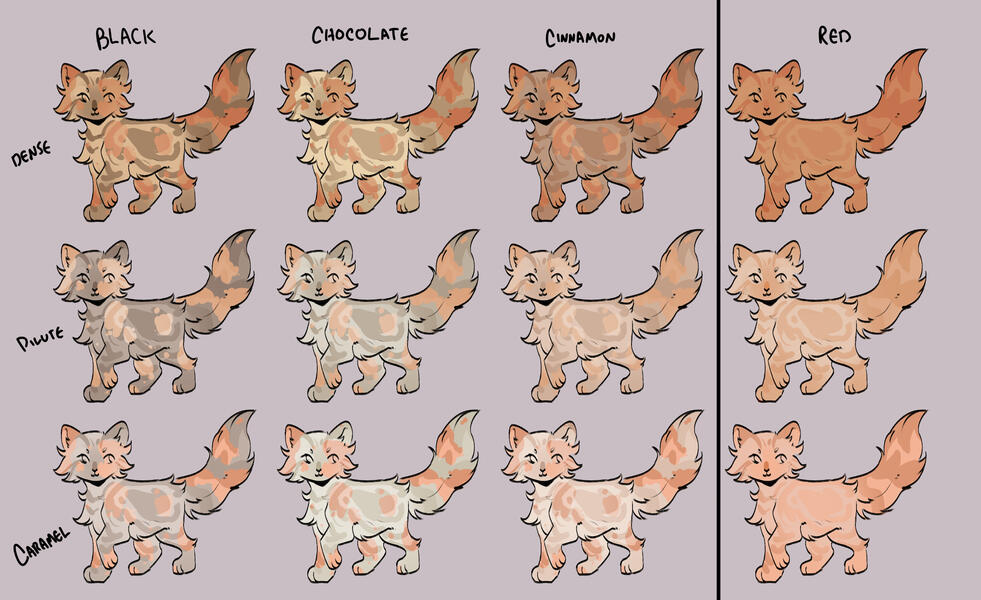
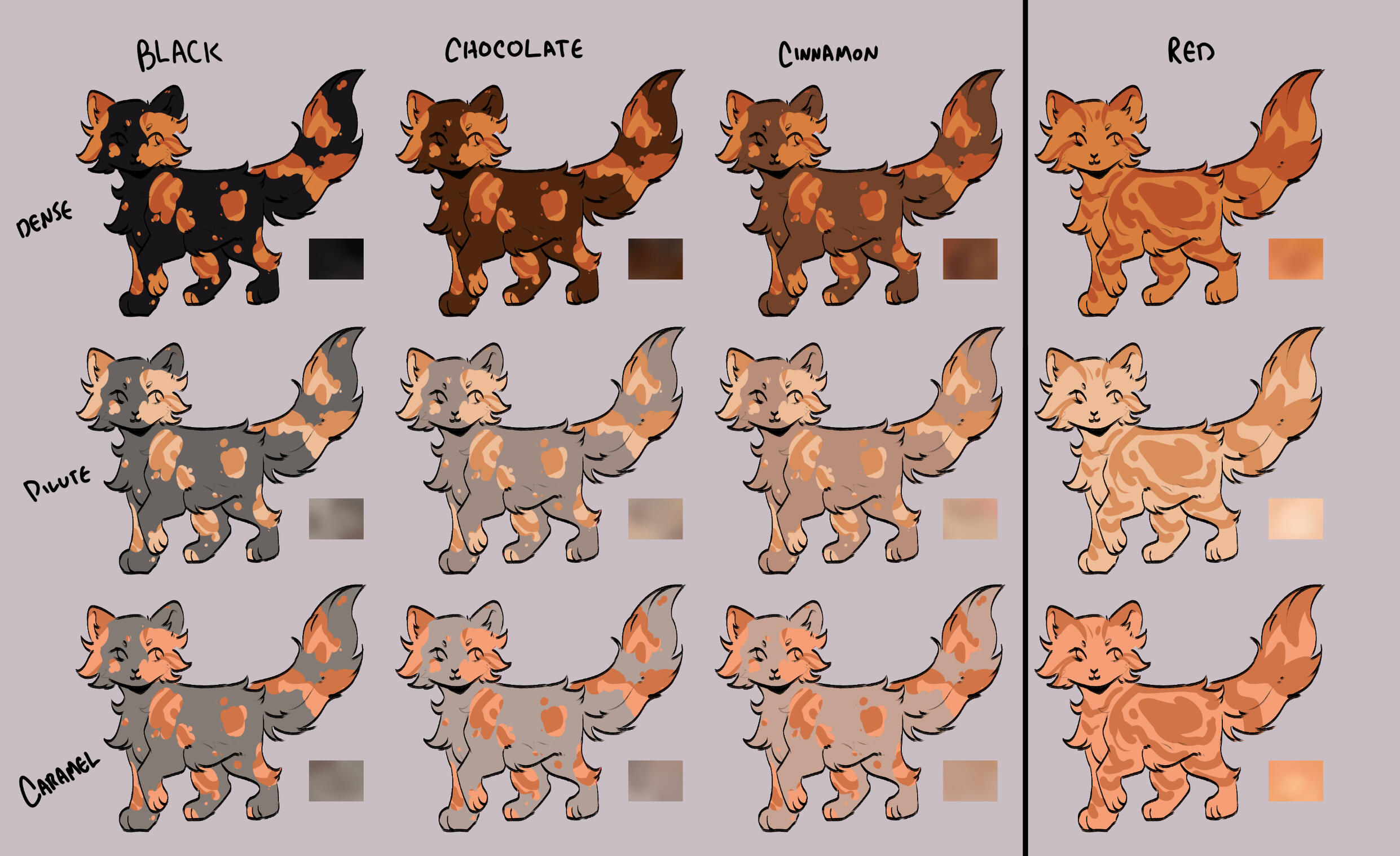
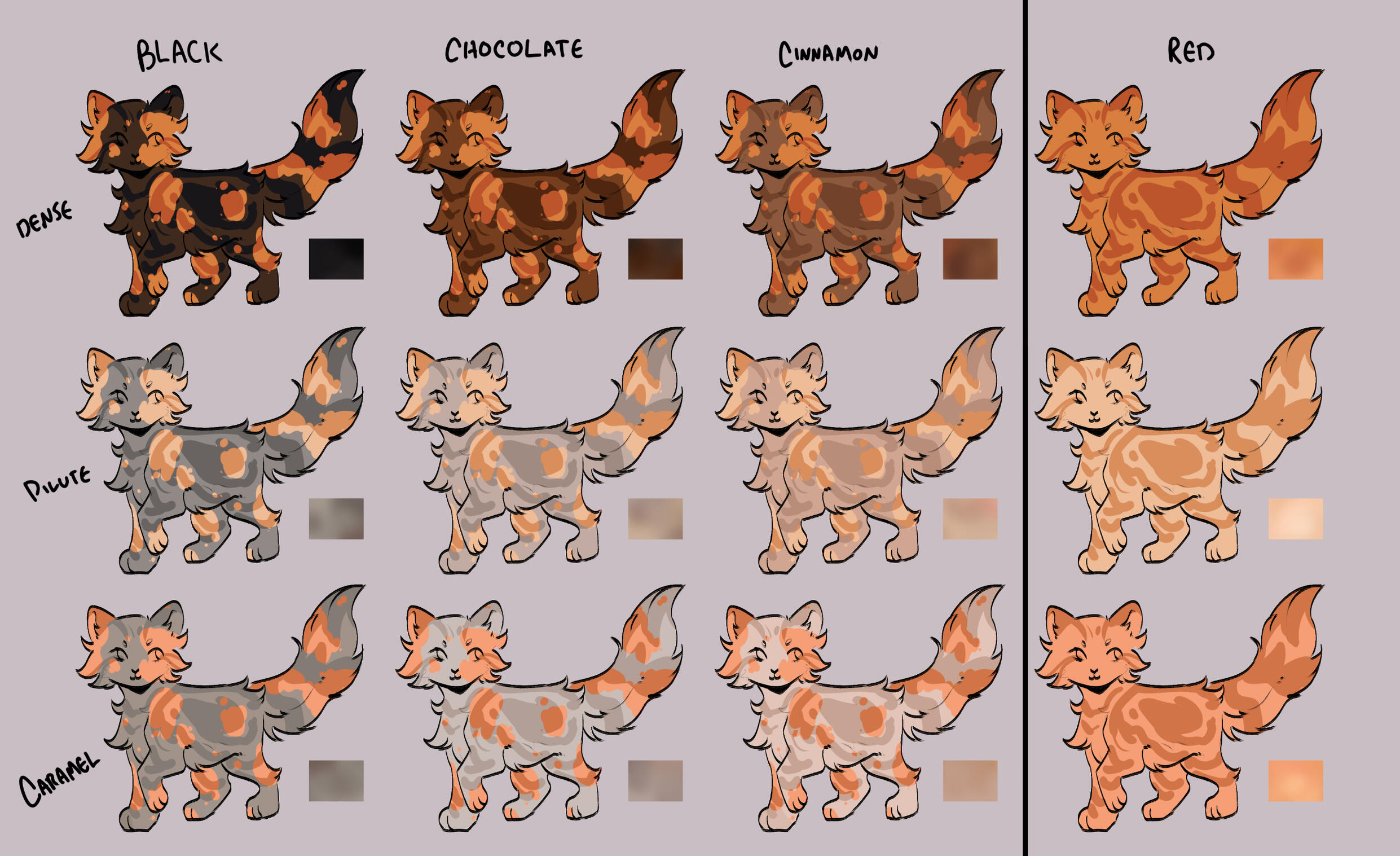
TORTIES/TORBIES
torties are genetically solid. they will ALWAYS have tabby markings on the 'red' spots. (this is because reds will always show tabby markings, even if genetically solid!)torbies are genetically tabby. they will have tabby markings on both their base and red.calicos/torbies/torties are always their dense black based colour + dense red.
for example:
- black-red
- blue-cream
- caramel-apricot


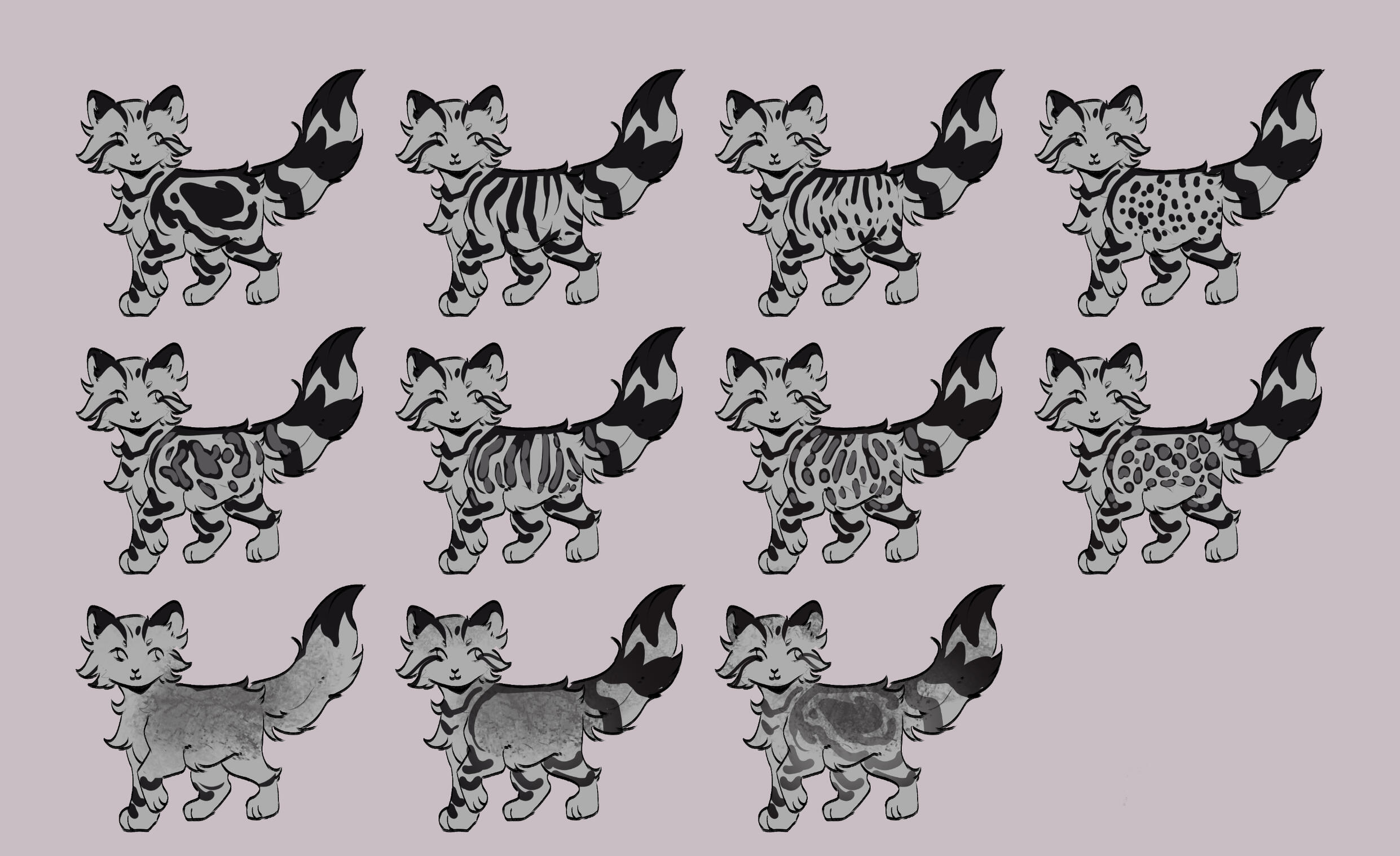
TABBY PATTERNS
we will go from left to right, in lines:Line One: Classic, Mackerel, Broken Braided
Line Two: Marbled, Broken Braided, Rosetted (wildtype modifiers)
Line Three: barless ticked, barred ticked, ticked breakthrough
POINTS
there is four different types we are focusing on: colourpoint, sepia, mink, and mocha. note mocha has two subtypes: burmocha and siamocha.you dont have to worry about mocha too too much, as mochas a more 'complicated' gene and undiscovered! many of the mocha visuals may not be right, as plenty dont exist in real life cats.** note, these visuals are up for redos to become more clear/accurate! most were made quickly, and therefor, inaccurate.